When choosing energy-efficient doors for your home, consider the material, insulation, and glass options. Fiberglass and steel doors with foam cores offer excellent insulation, while wood doors can be energy-efficient with proper construction. Look for doors with an R-value of at least R-5 for optimal efficiency. Double or triple-paned glass with low-E coatings and argon gas can improve insulation. Don't forget about weatherstripping and proper installation to prevent air leakage. Storm doors can add an extra layer of insulation to your entry door. By understanding these factors, you'll be better equipped to make an informed decision that saves energy and money.
Types of Energy-Efficient Doors

When it comes to energy-efficient doors, you'll find several options to choose from. The most common types include fiberglass, steel, and wood doors, each with unique energy-saving properties.
Fiberglass doors offer excellent insulation and durability. They're resistant to warping and cracking, maintaining their energy efficiency over time. You can find fiberglass doors with foam cores that provide superior insulation.
Steel doors are another energy-efficient option. They're strong, secure, and can be filled with foam insulation for better thermal performance. Steel doors are also low-maintenance and can be painted to match your home's exterior.
Wood doors, while traditional, can be energy-efficient when properly constructed. Look for solid wood cores or engineered wood with insulating materials. Ensure they're properly sealed and weatherstripped to prevent air leakage.
For maximum energy efficiency, consider double or triple-paned glass if your door includes windows. Low-E coatings and argon gas between panes can further improve insulation.
Don't forget about storm doors. They add an extra layer of insulation and can improve your door's energy efficiency, especially for older entry doors.
Material Considerations
While selecting an energy-efficient door, you'll need to carefully consider the materials used in its construction. The most common materials for energy-efficient doors are wood, fiberglass, and steel. Each has its unique properties and benefits.
Wood doors offer natural insulation and aesthetic appeal but require regular maintenance to prevent warping and rotting. They're best suited for protected areas. Fiberglass doors are highly durable, resist dents and scratches, and can mimic the look of wood. They're low-maintenance and provide excellent insulation. Steel doors are the most secure option and offer good insulation when properly constructed with an insulating core. They're durable but can dent and may rust if the protective coating is compromised.
Consider the door's core material as well. Polyurethane foam cores provide superior insulation compared to polystyrene. Some doors feature a combination of materials, such as a wood frame with fiberglass panels, offering a balance of aesthetics and energy efficiency. Don't forget to factor in the climate of your area when choosing materials. For instance, in humid regions, fiberglass might be a better choice than wood due to its moisture resistance.
Insulation and R-Values
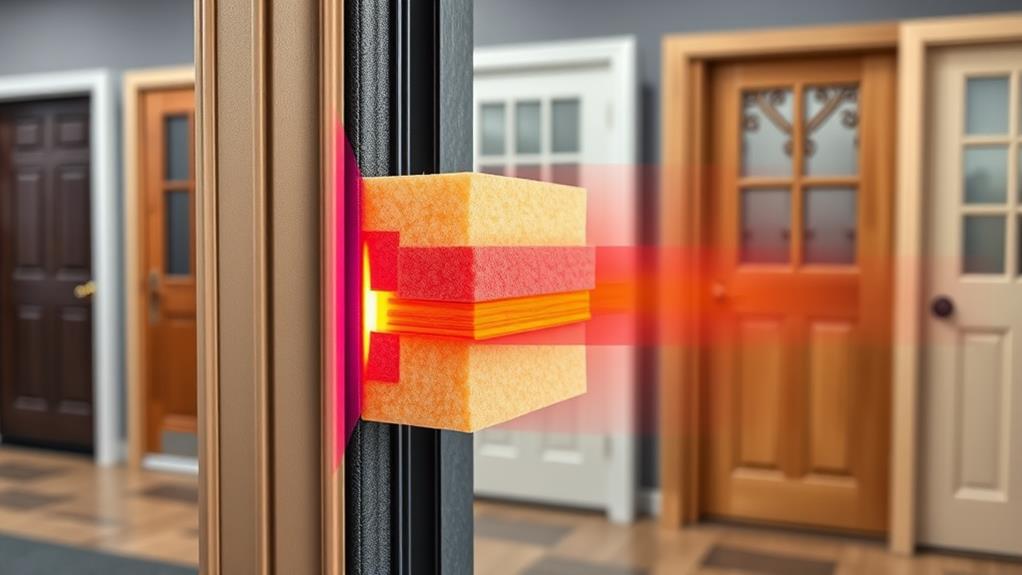

Two key factors in determining a door's energy efficiency are its insulation and R-value. The R-value measures a door's resistance to heat flow, with higher values indicating better insulation. For optimal energy efficiency, you'll want to look for doors with an R-value of at least R-5.
When selecting a door, consider its core material. Foam-core doors offer excellent insulation, typically ranging from R-5 to R-13. Solid wood doors, while aesthetically pleasing, have lower R-values around R-2 to R-3. Fiberglass and steel doors with polyurethane foam cores can provide R-values up to R-6.
Don't forget about weatherstripping and proper installation. Even the most insulated door won't perform well if it's not sealed correctly. Look for doors with built-in weatherstripping or add your own to prevent air leaks.
Glass panels in doors can significantly reduce their overall R-value. If you want a door with windows, opt for double or triple-paned glass with low-emissivity coatings to maintain better insulation.
Weatherstripping and Seals
Weatherstripping and seals play a crucial role in enhancing your door's energy efficiency. They prevent air leakage around the door's edges, reducing heat loss in winter and cool air escape in summer. When choosing weatherstripping, consider durability, ease of installation, and compatibility with your door type.
For the bottom of your door, install a door sweep or threshold seal. These come in various materials like rubber, vinyl, or brush-style. Ensure a snug fit without impeding the door's operation.
For the sides and top, you'll find options like adhesive-backed foam tape, V-strip weatherstripping, or tubular rubber gaskets.
Don't forget to seal the gap between the door frame and the wall. Use caulk or expanding foam to fill any cracks, preventing drafts and moisture infiltration. Regularly inspect your weatherstripping for wear and tear, replacing it as needed to maintain optimal performance.
When installing new doors, look for models with built-in weatherstripping. These often provide superior sealing and require less maintenance. Remember, proper installation is key to ensuring your weatherstripping and seals function effectively, so consider professional installation if you're unsure about DIY methods.
Glass Options for Doors
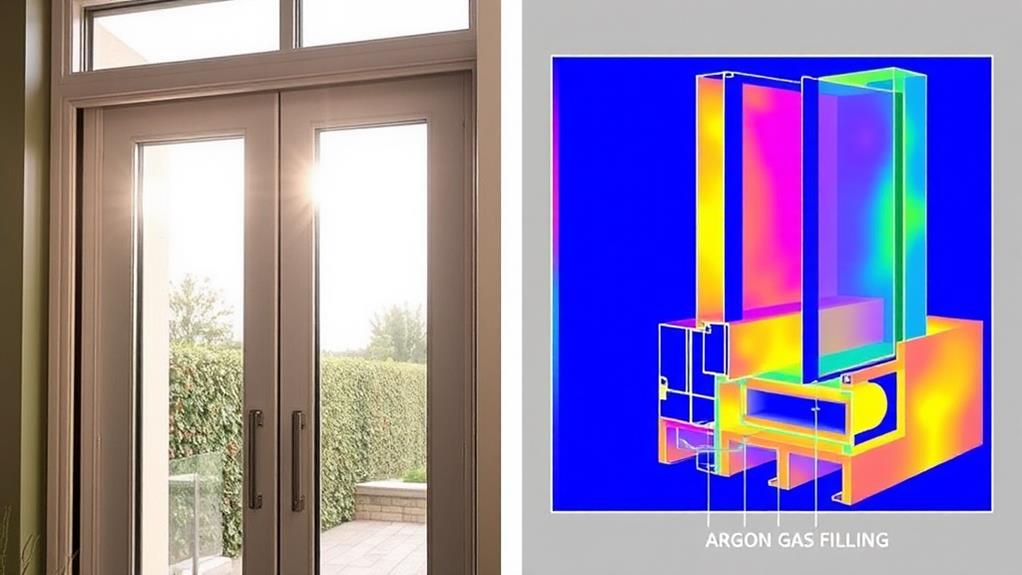
When it comes to glass options for doors, you'll find a wide array of choices that can impact both aesthetics and energy efficiency. Single-pane glass is the least energy-efficient option, while double-pane and triple-pane glass offer better insulation. These multi-pane options often include inert gases like argon or krypton between the panes, further enhancing their insulating properties.
Low-emissivity (low-E) coatings are another important feature to consider. These microscopically thin metal layers reflect heat while allowing light to pass through, helping to keep your home cooler in summer and warmer in winter. You can also opt for tinted glass, which reduces solar heat gain and glare, or reflective glass that bounces sunlight away from your home.
For maximum energy efficiency, look for glass doors with warm-edge spacers, which minimize heat transfer around the edges of the glass panels. Additionally, consider the U-factor and Solar Heat Gain Coefficient (SHGC) ratings when selecting glass doors. Lower U-factor values indicate better insulation, while lower SHGC values mean less solar heat transmission. By choosing the right glass options, you'll improve your door's energy performance and enhance your home's comfort.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation techniques are crucial for maximizing your door's energy efficiency. To ensure optimal performance, start by carefully measuring the door opening and purchasing a door that fits precisely. Before installation, inspect the frame for any damage or rot, and repair or replace it if necessary. Apply weatherstripping around the entire perimeter of the door frame to create an airtight seal.
When installing the door, use shims to level and plumb it, ensuring a snug fit. Fill any gaps between the frame and rough opening with low-expansion foam insulation. Be careful not to over-expand the foam, as this can warp the frame. Install a properly fitting threshold and door sweep to prevent drafts from entering underneath.
For sliding glass doors, pay special attention to the track system. Clean it thoroughly and apply lubricant to ensure smooth operation. Double-check that the door locks securely and that there are no gaps when closed. Finally, caulk around the exterior trim to prevent water infiltration. By following these installation best practices, you'll significantly improve your door's energy efficiency and overall performance.
Conclusion
You've now got the knowledge to choose energy-efficient doors that'll keep your home cozy and your energy bills low. While the initial cost might seem high, remember that you'll recoup your investment through years of savings. Don't let sticker shock deter you from making a smart, long-term decision. By selecting the right materials, insulation, and glass options, and ensuring proper installation, you'll enjoy a more comfortable and eco-friendly home for years to come.

