Heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) offer a dual benefit for your home: improved indoor air quality and energy savings. They work by exchanging stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air while transferring heat between the two streams. You'll enjoy cleaner air, consistent humidity levels, and lower utility bills. HRVs are ideal for newly built or tightly sealed homes, cold climates, and areas with poor outdoor air quality. Regular maintenance, including filter changes and vent cleaning, keeps your system running efficiently. Compared to other ventilation options, HRVs provide a balanced approach to fresh air and energy conservation. Discover how this innovative technology can transform your living space.
How Heat Recovery Ventilators Work
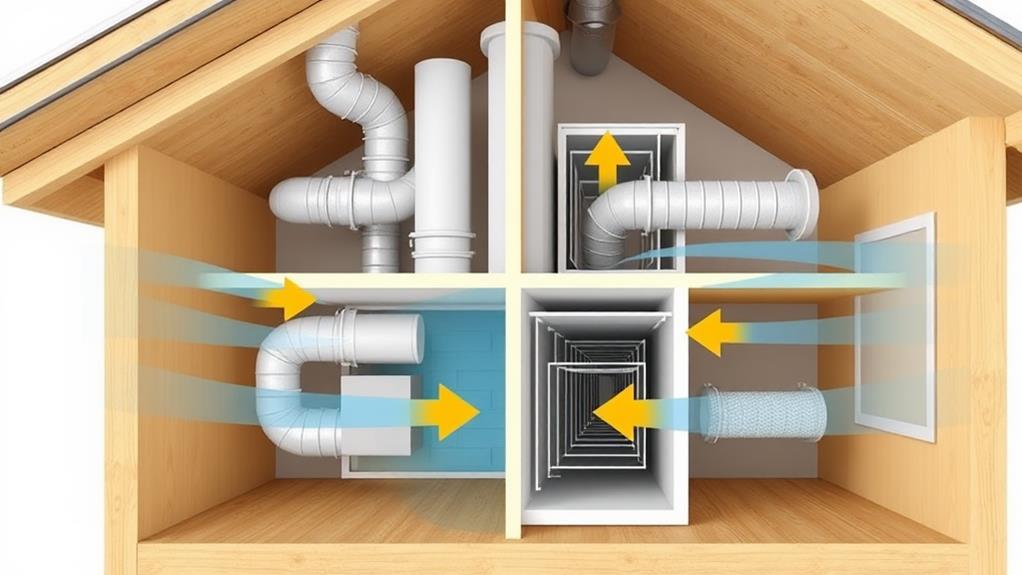
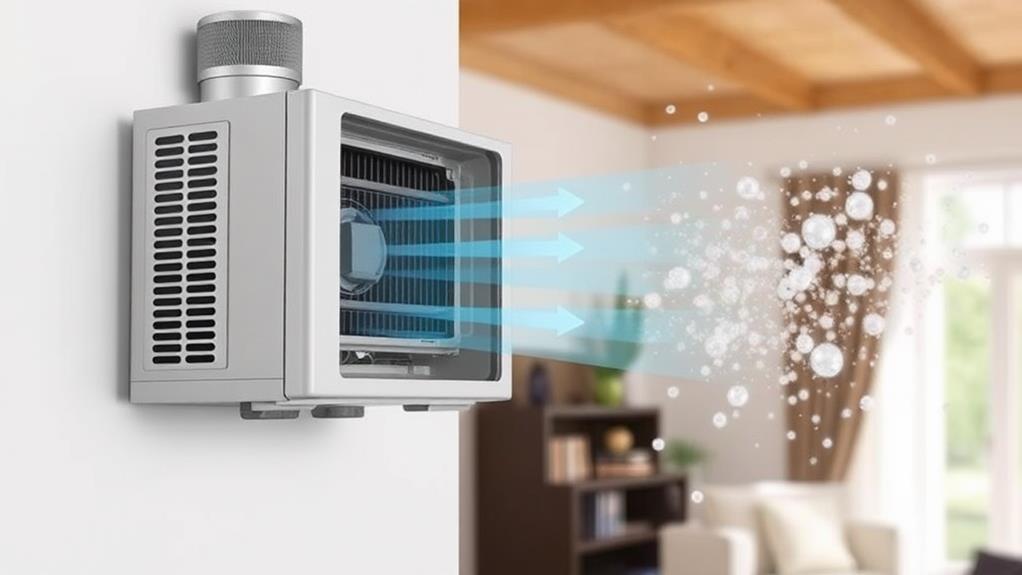
Inside of a heat recovery ventilator (HRV), two separate airstreams flow past each other without mixing. One stream consists of stale indoor air being exhausted, while the other is fresh outdoor air being brought in. As these airstreams pass through the HRV's core, heat is transferred from the warmer stream to the cooler one.
In winter, the outgoing warm air preheats the incoming cold air. This process recovers up to 85% of the heat that would otherwise be lost. During summer, the reverse occurs, with the cooler indoor air pre-cooling the warmer incoming air. This heat exchange helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature while reducing the load on your heating and cooling systems.
HRVs use fans to move air through the system and filters to remove pollutants. Some models include humidity sensors to adjust ventilation rates based on indoor moisture levels. You'll typically find HRVs installed in attics, basements, or utility rooms, with ductwork connecting them to your home's various rooms. By continuously exchanging air, HRVs ensure a steady supply of fresh air while minimizing energy loss, making them an efficient solution for improving indoor air quality and reducing energy costs.
Benefits of Installing an HRV
Installing a heat recovery ventilator offers three major benefits for homeowners. First, you'll enjoy improved indoor air quality. An HRV continuously exchanges stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air, removing pollutants, allergens, and excess moisture. This results in a healthier living environment, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and mold growth.
Second, you'll save energy and lower your utility bills. HRVs recover up to 85% of the heat from outgoing air, transferring it to incoming fresh air. This means your heating and cooling systems won't have to work as hard to maintain comfortable temperatures, leading to significant energy savings throughout the year.
Lastly, you'll enhance your home's comfort. HRVs help maintain consistent humidity levels, eliminating issues like condensation on windows and stuffy rooms. They also reduce outdoor noise infiltration, creating a quieter indoor environment. Additionally, by providing a constant supply of fresh air, HRVs eliminate the need to open windows, which can compromise your home's security and introduce unwanted pollen or pollutants. Overall, installing an HRV is a smart investment that improves your home's air quality, energy efficiency, and comfort.
Ideal Applications for HRVs
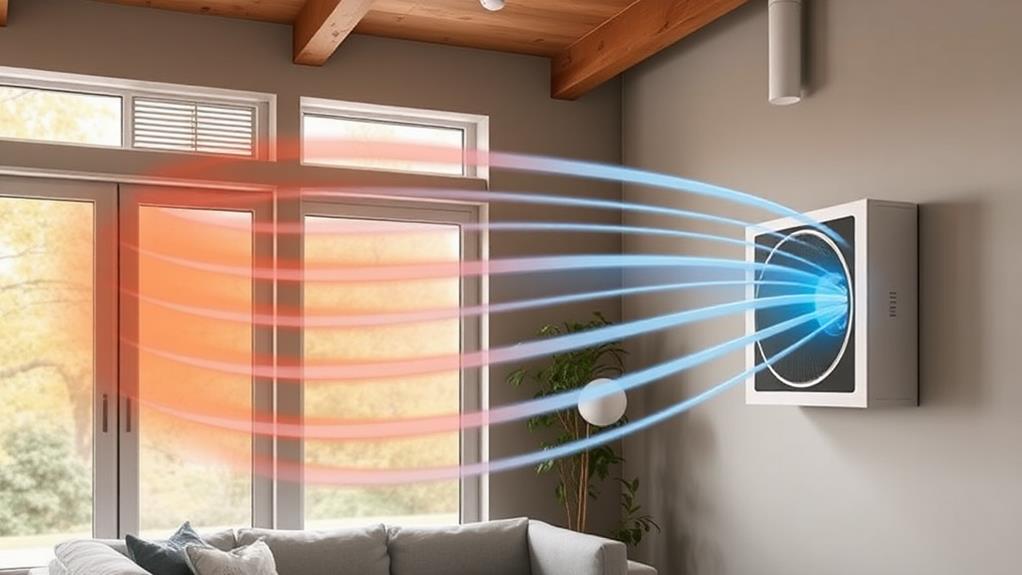
Heat recovery ventilators are particularly well-suited for certain types of homes and buildings. You'll find HRVs most beneficial in newly constructed or tightly sealed homes, where air exchange with the outdoors is limited. These energy-efficient structures often trap indoor pollutants, making mechanical ventilation crucial for maintaining healthy air quality.
HRVs excel in cold climates, where they can significantly reduce heating costs by recovering warmth from exhaust air. They're also ideal for humid regions, as they help control moisture levels indoors. If you live in an area with poor outdoor air quality or high pollen counts, an HRV with proper filtration can improve your indoor environment.
Consider installing an HRV if you have a large household or frequently host gatherings, as these systems effectively remove excess CO2 and odors. They're also excellent for homes with attached garages, basements, or other areas prone to pollutant buildup. If you or your family members suffer from allergies or respiratory issues, an HRV can provide consistent fresh air circulation, potentially alleviating symptoms. Lastly, HRVs are perfect for homeowners committed to energy efficiency and sustainability, as they maintain indoor comfort while minimizing energy waste.
Maintenance and Operation Tips
To ensure your HRV continues to perform optimally, regular maintenance is key. Clean or replace air filters every three months, or more frequently if you live in a dusty area. Inspect the exterior vents twice a year, removing any debris or obstructions that could impede airflow. Check and clean the heat exchange core annually, following the manufacturer's instructions carefully.
Don't forget to clean the condensate drain regularly to prevent clogs and potential water damage. Lubricate moving parts, such as fan motors, as recommended by the manufacturer. During operation, keep your HRV running continuously on a low setting to maintain consistent indoor air quality. Adjust the fan speed higher during activities that generate more indoor pollutants, like cooking or showering.
In winter, you may need to defrost your HRV occasionally. Most units have an automatic defrost cycle, but check your manual for specific instructions. Monitor your energy bills to ensure your HRV is operating efficiently. If you notice a significant increase in energy consumption, it may indicate a problem that requires professional attention. By following these maintenance and operation tips, you'll maximize your HRV's performance and lifespan.
Comparing HRVs to Other Ventilation Systems
When it comes to ventilation systems, HRVs aren't the only game in town. You'll find several alternatives, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Exhaust-only systems, like bathroom fans, are simple and inexpensive but don't recover heat or filter incoming air. Supply-only systems, such as kitchen range hoods, bring in fresh air but can create pressure imbalances and don't recover heat either.
Balanced ventilation systems, including energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), offer similar benefits to HRVs. ERVs transfer both heat and moisture, making them ideal for humid climates. However, they're typically more expensive and complex than HRVs.
Natural ventilation, relying on open windows and building design, is cost-free but unreliable and can't filter air or recover heat. Mechanical ventilation without heat recovery, like standard HVAC systems, provides consistent airflow but wastes energy.
HRVs stand out for their ability to maintain indoor air quality while conserving energy. They're particularly effective in cold climates where heat loss is a significant concern. While more expensive upfront than some alternatives, HRVs can offer long-term savings through reduced energy costs and improved indoor air quality.
Conclusion
You've now learned the ins and outs of heat recovery ventilators. They're not just a flash in the pan – these energy-saving marvels are here to stay. By installing an HRV, you'll breathe easier, save money, and reduce your carbon footprint. It's like having your cake and eating it too! So don't be a stick in the mud. Embrace this technology and enjoy the benefits of fresh, clean air in your home year-round.

