Heat pumps offer a versatile solution for both heating and cooling your home. They work by transferring heat from one place to another, providing warmth in winter and coolness in summer. You'll find various types, including air-source, ground-source, and water-source heat pumps, each suited to different environments. These systems are highly energy-efficient, potentially cutting your heating costs by 30-60% compared to electric resistance heating. They're also environmentally friendly, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and your carbon footprint. With proper installation and maintenance, heat pumps can provide long-lasting comfort and savings. Discover how this innovative technology can revolutionize your home's climate control.
How Heat Pumps Work
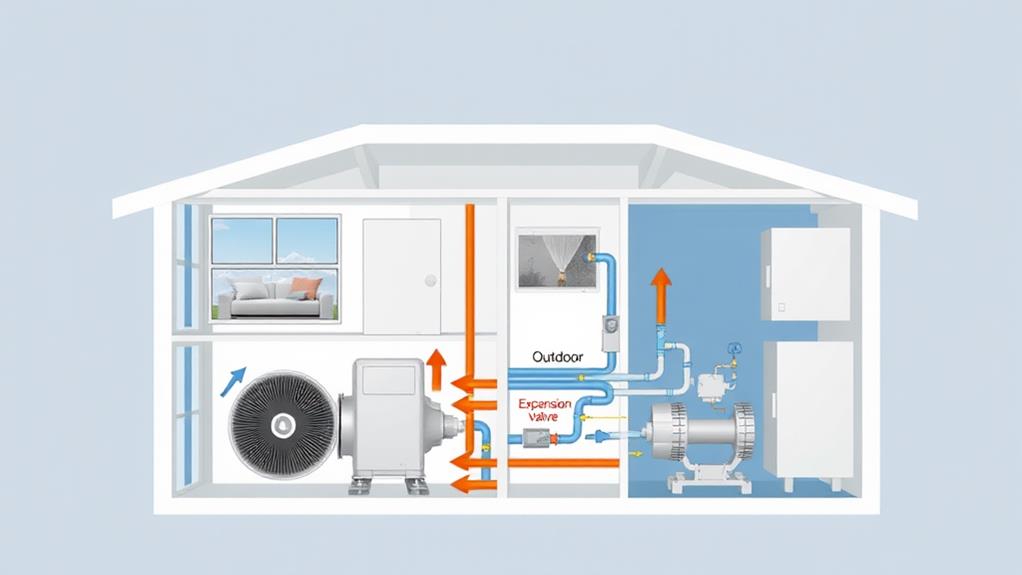
How do heat pumps manage to both heat and cool your home? It's all about transferring heat, rather than generating it. In cooling mode, a heat pump works like an air conditioner, extracting heat from inside your home and releasing it outside. In heating mode, it reverses this process, capturing heat from the outdoor air (even in cold weather) and moving it indoors.
The key components of a heat pump include a compressor, two heat exchanger coils (one indoor and one outdoor), and a reversing valve. Refrigerant circulates through these components, changing state between liquid and gas to absorb and release heat. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, while the coils facilitate heat exchange with the air.
When heating, the outdoor coil acts as an evaporator, absorbing heat from the air. The compressed refrigerant then moves to the indoor coil, where it condenses and releases heat into your home. For cooling, the process reverses, with the indoor coil absorbing heat and the outdoor coil releasing it. This versatile operation makes heat pumps an efficient, year-round climate control solution.
Types of Heat Pumps
There are three main types of heat pumps you'll encounter in residential settings: air-source, ground-source (geothermal), and water-source.
Air-source heat pumps are the most common and cost-effective option. They extract heat from outdoor air and transfer it inside during winter, reversing the process for cooling in summer. These units work well in moderate climates but may struggle in extreme temperatures.
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal systems, use the earth's constant underground temperature to heat and cool your home. They're more expensive to install but offer higher efficiency and lower operating costs over time. You'll need sufficient land for the underground loop system.
Water-source heat pumps operate similarly to ground-source systems but use a nearby water body as the heat source or sink. They're ideal if you have access to a pond, lake, or well. These systems are highly efficient but require specific site conditions.
Each type has its pros and cons, so you'll need to consider factors like climate, property characteristics, and budget when choosing the best heat pump for your home. Consult with a professional to determine which option suits your needs.
Energy Efficiency Benefits

Understanding the different types of heat pumps sets the stage for appreciating their remarkable energy efficiency benefits. Heat pumps offer significant energy savings compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. They can provide up to 3-4 times more energy than they consume, making them an excellent choice for environmentally conscious homeowners.
You'll notice a reduction in your energy bills when using a heat pump. These systems transfer heat rather than generate it, resulting in lower energy consumption. In moderate climates, heat pumps can cut your heating costs by 30-60% compared to electric resistance heating.
Heat pumps also excel in cooling mode, often surpassing the efficiency of standard air conditioners. Their ability to both heat and cool eliminates the need for separate systems, reducing overall energy use and maintenance costs.
Additionally, heat pumps contribute to reduced carbon emissions. By using electricity more efficiently and potentially drawing from renewable sources, you're lowering your carbon footprint. Some governments offer incentives for installing heat pumps, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits.
Cost Savings Over Time
While the initial cost of a heat pump may seem steep, you'll find that the long-term savings are substantial. Over time, you'll recoup your investment through lower energy bills and reduced maintenance costs. Heat pumps typically use less energy than traditional heating and cooling systems, resulting in significant savings on your monthly utility expenses.
You'll notice the difference in your wallet almost immediately. Depending on your local energy prices and climate, you could save anywhere from 30% to 60% on your heating costs compared to electric resistance heating. In cooling mode, heat pumps are often more efficient than standard air conditioners, further reducing your energy consumption.
The longevity of heat pumps also contributes to their cost-effectiveness. With proper maintenance, a quality heat pump can last 15 to 20 years, outlasting many conventional HVAC systems. This extended lifespan means you'll avoid frequent replacement costs. Additionally, some regions offer tax incentives or rebates for installing energy-efficient heat pumps, which can help offset the initial purchase price. When you factor in these benefits, you'll see that a heat pump is a wise financial decision for your home's heating and cooling needs.
Environmental Impact

Heat pumps consistently offer significant environmental benefits compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. They're highly efficient, using electricity to transfer heat rather than generate it, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. You'll find that heat pumps can be up to 300% efficient, meaning they produce three units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed.
By choosing a heat pump, you're reducing your carbon footprint significantly. Unlike fossil fuel-based systems, heat pumps don't burn fuel directly, eliminating on-site emissions. When paired with renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, they can provide nearly carbon-neutral heating and cooling.
Heat pumps also help reduce the demand for fossil fuels, contributing to energy independence and security. They're particularly beneficial in areas where electricity is generated from clean sources. Additionally, heat pumps use refrigerants with lower global warming potential than those in traditional air conditioners, further minimizing their environmental impact. As regulations tighten on harmful refrigerants, heat pump technology continues to evolve, adopting even more environmentally friendly options. By installing a heat pump, you're making a long-term investment in sustainable home comfort.
Installation Considerations
When considering a heat pump for your home, it's important to evaluate several installation factors. First, assess your home's insulation and air sealing. A well-insulated house will maximize the heat pump's efficiency.
You'll also need to determine the appropriate size and type of heat pump for your space. An undersized unit won't meet your needs, while an oversized one will cycle on and off too frequently.
Consider the location for both indoor and outdoor units. The indoor unit should be centrally located for even distribution, while the outdoor unit needs proper clearance and protection from elements. You'll also need to decide between a ducted or ductless system, depending on your home's existing infrastructure.
Electrical requirements are crucial. Heat pumps may need a dedicated circuit or electrical panel upgrade. Additionally, you should check local building codes and obtain necessary permits. It's wise to hire a qualified HVAC professional for installation, as proper setup ensures optimal performance and longevity. They can also advise on complementary systems, like backup heating for extremely cold climates.
Lastly, consider the potential need for landscaping adjustments to accommodate the outdoor unit.
Maintenance and Longevity

Regularly maintaining your heat pump is crucial for ensuring its longevity and optimal performance. You'll need to clean or replace air filters every 1-3 months, depending on usage and environmental factors. Keep the outdoor unit free from debris, leaves, and snow to maintain proper airflow.
Inspect and clean the evaporator and condenser coils annually to prevent buildup that can reduce efficiency.
Don't forget to check refrigerant levels and look for leaks during your annual maintenance. Low refrigerant can strain the system and decrease its effectiveness. You should also inspect electrical connections and tighten them if necessary to prevent safety hazards and improve performance.
With proper care, your heat pump can last 15-20 years. However, you may need to replace the compressor or other major components after 10-15 years. Pay attention to signs of declining performance, such as inconsistent temperatures, strange noises, or increased energy bills. These may indicate it's time for repairs or replacement. By staying proactive with maintenance, you'll extend your heat pump's lifespan and ensure it operates efficiently throughout its service life.
Adapting to Different Climates
Climate versatility is a key advantage of heat pumps. You'll find these systems can operate efficiently in various environments, from scorching summers to frigid winters.
In moderate climates, heat pumps excel year-round, providing both heating and cooling with minimal energy consumption.
For colder regions, you'll want to consider cold-climate heat pumps. These specialized units maintain efficiency even when temperatures drop well below freezing. They're designed with enhanced compressors and refrigerants that perform optimally in harsh winter conditions.
In hot, humid climates, heat pumps offer excellent dehumidification capabilities alongside cooling. You'll benefit from improved indoor air quality and comfort. Some models come with variable-speed compressors, allowing for precise temperature and humidity control.
Coastal areas present unique challenges due to salt air corrosion. You should opt for heat pumps with corrosion-resistant coatings and components to ensure longevity in these environments.
For areas prone to extreme weather events, look for heat pumps with robust designs that can withstand high winds and heavy rainfall. Some manufacturers offer models specifically engineered for hurricane-prone regions.
Choosing the Right System
Selecting the right heat pump system for your home involves considering several key factors. First, assess your climate and heating needs. If you live in a moderate climate, an air-source heat pump might suffice. For colder regions, you'll want to consider a ground-source or water-source system for better efficiency.
Next, evaluate your home's size and insulation. A properly sized system ensures optimal performance and energy savings. Don't forget to factor in your budget, as initial costs can vary significantly between different types of heat pumps.
Consider the available space for installation. Air-source units require outdoor space for the compressor, while ground-source systems need land for underground loops. If you're retrofitting an existing home, ductless mini-split systems might be a good option.
Energy efficiency ratings are crucial. Look for SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings to compare systems. Higher numbers indicate better efficiency.
Lastly, consult with a qualified HVAC professional. They can help you navigate local regulations, available incentives, and specific installation requirements to ensure you choose the most suitable heat pump system for your needs.
Conclusion
You've discovered that heat pumps are like Swiss Army knives for home comfort—versatile and efficient. They'll keep you cozy in winter and cool in summer while slashing your energy bills and carbon footprint. Whether you're in a frosty mountain town or a sweltering coastal city, there's a heat pump system that's right for you. With proper installation and maintenance, you'll enjoy years of reliable, eco-friendly heating and cooling.

