Proper ventilation is essential in preventing mold growth by controlling moisture levels and maintaining healthy indoor air quality. Effective airflow reduces humidity, which is crucial as mold thrives in damp environments. Ventilation systems, including exhaust fans, dehumidifiers, and HVAC units, work together to remove excess moisture and circulate fresh air throughout a building. Key areas requiring particular attention include bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and attics. Implementing ventilation best practices, such as regular maintenance and ensuring adequate air exchange, significantly reduces the risk of mold development. By balancing energy efficiency with proper airflow, homeowners can create an environment that is inhospitable to mold while maintaining comfort and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding Mold Growth Conditions

To effectively prevent mold growth, it is crucial to understand the conditions that promote its development. Mold thrives in environments with excess moisture, moderate temperatures, and organic material as a food source. Humidity levels above 60% create an ideal breeding ground for mold spores, which are naturally present in the air. Areas with poor air circulation and limited sunlight exposure are particularly susceptible to mold growth.
Common sources of moisture that contribute to mold problems include leaky pipes, roof damage, condensation on windows, and high indoor humidity. Organic materials such as wood, paper, fabric, and drywall serve as nutrient-rich substrates for mold. Temperatures between 60°F and 80°F (15°C to 27°C) are optimal for most mold species, though some can grow in colder or warmer conditions.
Understanding these growth factors is essential for implementing effective prevention strategies. By controlling moisture levels, improving ventilation, and minimizing organic debris, property owners can significantly reduce the risk of mold infestation. Regular inspections and prompt addressing of water-related issues are key components of a comprehensive mold prevention plan.
Moisture Control Through Ventilation
Effective ventilation plays a crucial role in controlling moisture levels and preventing mold growth. By promoting air circulation and reducing humidity, proper ventilation helps create an environment unfavorable for mold spores to thrive. In areas prone to moisture accumulation, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements, adequate ventilation is essential.
Installing and maintaining exhaust fans in bathrooms and kitchens can significantly reduce moisture buildup from daily activities like showering and cooking. These fans should vent directly to the outside, not into attics or crawl spaces.
For basements and other damp areas, dehumidifiers can be used in conjunction with ventilation systems to maintain optimal humidity levels.
Natural ventilation through windows and doors can also be beneficial, especially in temperate climates. However, in humid environments, relying solely on natural ventilation may introduce more moisture into the home. In such cases, mechanical ventilation systems, such as whole-house fans or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs), can be more effective in controlling indoor humidity levels.
Regular maintenance of HVAC systems, including cleaning air ducts and replacing filters, ensures optimal performance in moisture control and mold prevention.
Types of Ventilation Systems
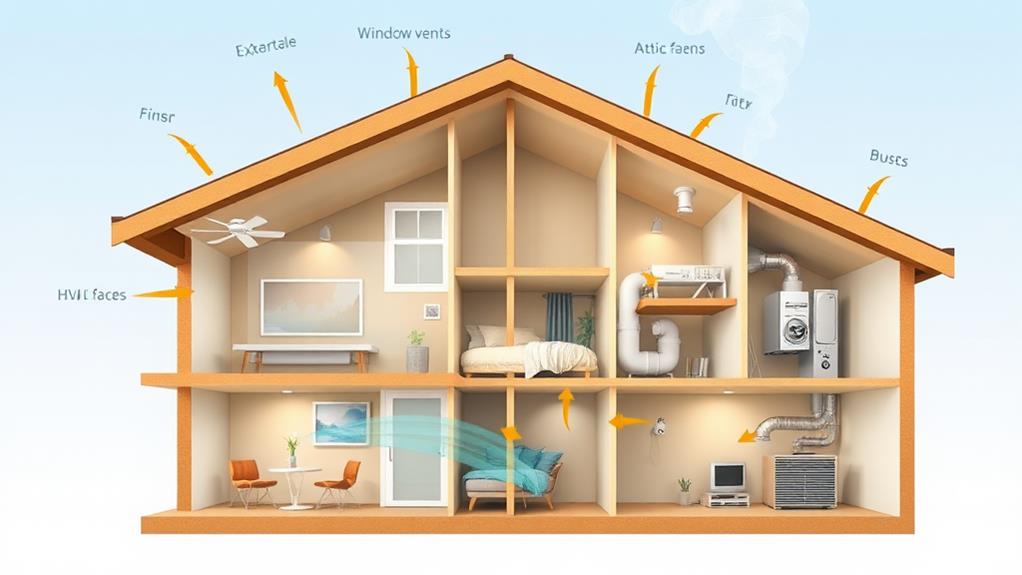
Various types of ventilation systems exist to address different moisture control needs and building configurations. The most common types include natural ventilation, mechanical ventilation, and hybrid systems.
Natural ventilation relies on passive airflow through windows, doors, and other openings. It's cost-effective but can be inconsistent and affected by external factors like weather. Mechanical ventilation uses fans and ducts to actively move air. This includes exhaust-only systems, which expel stale air, and supply-only systems, which introduce fresh air. Balanced systems combine both exhaust and supply functions for optimal air exchange.
More advanced options include heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and energy recovery ventilators (ERVs). These systems transfer heat between incoming and outgoing air streams, improving energy efficiency. Spot ventilation, such as bathroom fans or kitchen range hoods, targets specific high-moisture areas.
Whole-house ventilation systems provide comprehensive air exchange throughout the entire living space. These can be integrated with HVAC systems for better control and efficiency. The choice of ventilation system depends on factors like climate, building design, occupancy, and local regulations.
Key Areas Requiring Proper Airflow
While all areas of a home benefit from proper ventilation, certain spaces are particularly susceptible to moisture accumulation and require special attention. Bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms are prime areas for mold growth due to their high humidity levels and frequent water usage. These spaces need adequate ventilation to remove excess moisture and prevent condensation on surfaces.
Basements and crawl spaces are also critical areas for proper airflow. These below-grade areas are prone to dampness and often have poor natural ventilation. Installing dehumidifiers and ensuring proper air circulation can help mitigate moisture issues and discourage mold growth.
Attics and roof spaces require careful consideration as well. Proper attic ventilation helps regulate temperature and moisture levels, preventing condensation on the underside of the roof and reducing the risk of mold formation.
Closets and storage areas, particularly those on exterior walls, can be problematic if not properly ventilated. Leaving space between stored items and walls, and using moisture-absorbing products can help maintain a drier environment.
Ventilation Best Practices

To implement effective ventilation strategies for mold prevention, homeowners should focus on several key practices. First, ensure proper use of exhaust fans in high-moisture areas like bathrooms and kitchens. Run these fans during and for 30 minutes after activities that generate moisture.
Install and maintain HVAC systems with adequate capacity for your home's size, using MERV 11 or higher rated filters to trap mold spores.
Regularly open windows and doors to promote cross-ventilation, especially on dry days. Use ceiling fans to improve air circulation throughout living spaces. In basements and crawl spaces, consider installing dehumidifiers and ensuring proper drainage to control moisture levels. For attics, implement ridge and soffit vents to allow for continuous airflow.
In closets and other enclosed spaces, use louvered doors or install small vents to prevent stagnant air. Consider whole-house ventilation systems like heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) or energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) for consistent air exchange. Lastly, maintain clean and unobstructed air vents, registers, and return air grilles to ensure optimal airflow throughout your home.
Signs of Inadequate Ventilation
Recognizing signs of inadequate ventilation is crucial for effective mold prevention in homes. Several indicators can alert homeowners to ventilation issues that may lead to mold growth. Persistent condensation on windows, mirrors, or other surfaces is a common sign of excess moisture in the air. Musty odors, particularly in enclosed spaces like closets or bathrooms, often indicate poor air circulation and potential mold growth.
Visible water stains on walls or ceilings suggest moisture accumulation, while peeling wallpaper or paint can result from high humidity levels. Increased allergy symptoms or respiratory issues among occupants may also signal ventilation problems.
In kitchens and bathrooms, lingering steam or fogged mirrors long after showers or cooking activities point to insufficient air exchange. Other signs include difficulty opening or closing doors and windows due to swelling, warped wood surfaces, and the presence of mildew on fabrics or leather items. Homeowners should also be aware of unusually high indoor humidity levels, which can be measured using a hygrometer. Regular inspection for these signs and prompt action to improve ventilation can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth and ensure a healthier living environment.
Balancing Energy Efficiency and Airflow

Striking a balance between energy efficiency and proper airflow presents a challenge for homeowners aiming to prevent mold growth. Modern building practices emphasize energy conservation, often resulting in tightly sealed homes that inadvertently restrict air circulation. While this approach reduces energy costs, it can create an environment conducive to mold development.
To address this issue, homeowners should implement strategies that maintain energy efficiency while ensuring adequate ventilation. Installing energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) can help exchange stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air without sacrificing thermal comfort. These systems recover heat from outgoing air to pre-condition incoming air, minimizing energy loss.
Additionally, programmable thermostats and smart home systems can automate ventilation schedules, activating exhaust fans or opening windows during optimal times. Using ceiling fans to improve air circulation and incorporating passive ventilation techniques, such as strategically placed vents or transom windows, can also enhance airflow without significantly impacting energy consumption. Regular HVAC maintenance, including cleaning ducts and replacing filters, ensures efficient operation while promoting healthy indoor air quality. By implementing these measures, homeowners can effectively balance energy efficiency and airflow, reducing the risk of mold growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Certain Paint Additives Help Prevent Mold Growth in High-Humidity Areas?
Yes, certain paint additives can help prevent mold growth in high-humidity areas. Anti-microbial additives, such as fungicides and biocides, can be incorporated into paints to inhibit mold and mildew growth on painted surfaces for extended periods of time.
How Does Outdoor Air Quality Affect Indoor Ventilation Strategies for Mold Prevention?
Like a city's lungs, outdoor air quality directly impacts indoor ventilation strategies. Poor outdoor air may necessitate filtration systems, while cleaner air allows for more natural ventilation. Striking a balance is crucial for effective mold prevention indoors.
Are There Any Plants That Can Naturally Improve Indoor Air Quality and Reduce Mold?
Several plants can enhance indoor air quality and help reduce mold, including spider plants, peace lilies, and snake plants. These natural air purifiers absorb moisture and filter toxins, creating a healthier indoor environment with reduced mold risk.
What Role Do Air Purifiers Play in Mold Prevention Alongside Proper Ventilation?
Studies show air purifiers can remove up to 99.97% of airborne particles. Air purifiers complement proper ventilation by filtering mold spores, reducing humidity, and improving overall air quality. They're especially effective in areas prone to moisture accumulation.
How Does Building Material Selection Impact Ventilation Needs for Mold Prevention?
Building material selection significantly impacts ventilation requirements for mold prevention. Porous materials like wood and drywall absorb moisture readily, necessitating more robust ventilation systems. Conversely, non-porous materials like concrete or metal may require less intensive ventilation to mitigate mold growth.
Conclusion
Proper ventilation plays a pivotal role in mold prevention, simultaneously addressing moisture control and air quality. By implementing effective ventilation systems and practices, homeowners and building managers can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth. Coincidentally, these efforts also contribute to improved indoor air quality and energy efficiency. Vigilance in monitoring humidity levels, maintaining airflow, and addressing problem areas swiftly creates an environment inhospitable to mold. Ultimately, a well-ventilated space promotes both structural integrity and occupant health.

